Navigating the world of vehicle finance: Lease Purchase unveiled
If you’re seeking a financial arrangement that combines aspects of both leasing and ownership, Lease Purchase could be the solution you’ve been searching for. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the intricacies of Lease Purchase, shedding light on what it is, how it operates, and the advantages and drawbacks associated with this unique finance option.
What is Lease Purchase?
Lease Purchase is a type of conditional sale agreement, distinguishing it from standard leasing or rental arrangements. With Lease Purchase, your regular payments closely resemble those of a lease or rental agreement, but with a significant twist – you have the opportunity to own the vehicle at the conclusion of the deal. Unlike traditional leasing, where you return the vehicle at the end, Lease Purchase positions you as the future owner.
How does lease purchase work?
The mechanics of Lease Purchase can be broken down into key components:
1. The Deposit: Typically, you’ll provide an upfront deposit, typically around 10% of the vehicle’s cost. A larger deposit reduces the amount you need to borrow and consequently, lowers your monthly payments.
2. Monthly Payments: Following the deposit, you’ll make a series of monthly payments, similar to a lease or rental agreement. These payments cover the cost of using the vehicle during the agreements term.
3. Balloon Payment or Deferred Sum: The distinctive feature of Lease Purchase is the presence of a “balloon payment” or deferred sum that you must pay at the end of the agreement to secure ownership. This sum is calculated based on factors like the vehicle’s age and mileage at the end of the contract.
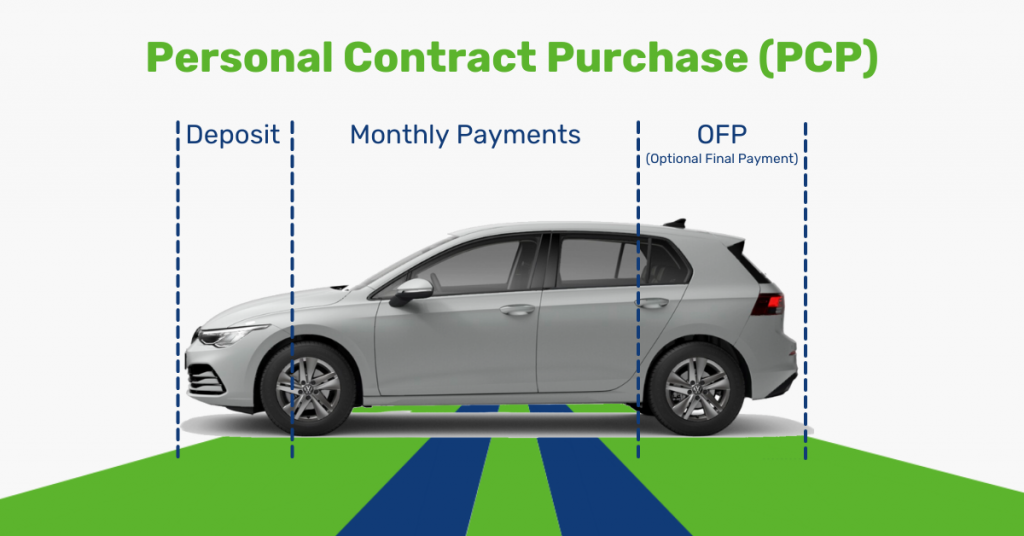
The balloon payment reflects the anticipated value of the vehicle at the agreement’s conclusion. It’s often a substantial sum, typically several thousand pounds, and it must be paid to complete the ownership transfer. Unlike Personal Contract Purchase (PCP), where you have choices at the end, Lease Purchase obligates you to make this payment to own the vehicle outright.
Options at the end of the agreement
While you’re committed to paying the balloon payment in Lease Purchase, you still have some flexibility:
- Refinancing: If paying the balloon sum in one go is challenging, you can explore refinancing or extending the agreement to make it more manageable.
- Selling the Vehicle: If you decide against keeping the vehicle, you have the option to sell it. Any equity generated for the sale remains with you.
The pros of lease purchase
-
Ownership Opportunity
Lease Purchase ultimately offers you the chance to become the vehicle's owner, making it an ideal choice if long-term ownership is your goal.
-
Low Initial Payments
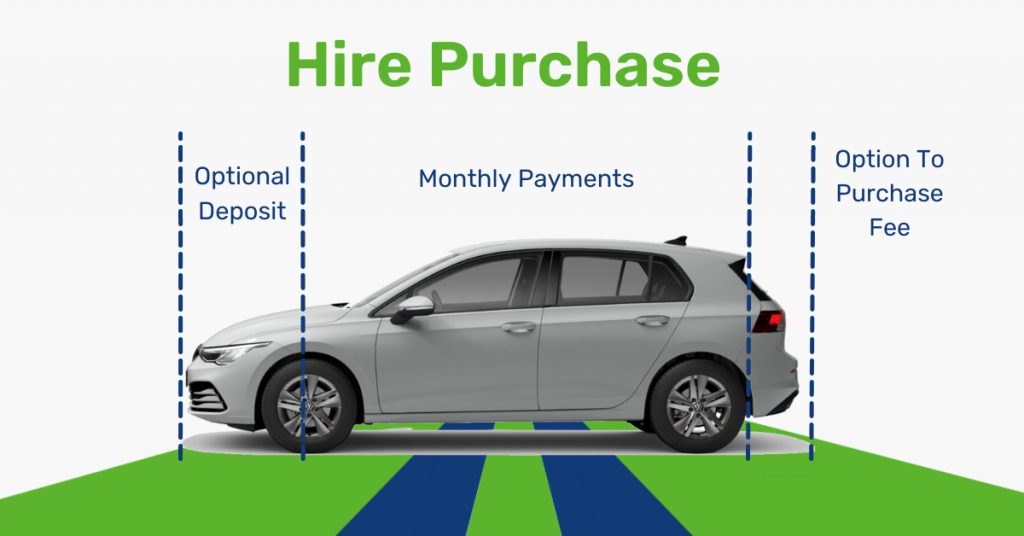
Lease Purchase typically requires lower initial payments compared to outright purchases or Hire Purchase agreements.
The Cons of Lease Purchase
-
Deferred Sum Obligation
The most significant drawback is the obligation to pay the balloon sum at the end of the agreement. Ownership is contingent on this payment.
-
Large Final Payment
The balloon payment can be substantial, and if not managed effectively, it may pose financial challenges.
Lease Purchase stikes a unique balance between leasing and ownership, offering the prospect of vehicle ownership while spreading the cost through manageable monthly payments. However, it’s crucial to understand that the substantial balloon payment is a mandatory requirement for ownership. If you’re seeking long-term vehicle ownership and can manage the deferred sum, Lease Purchase could be your path to driving your dream car.